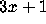 problem lies in the irregular behavior of the
successive iterates
problem lies in the irregular behavior of the
successive iterates 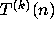 .
One can measure this behavior using the stopping time, the total stopping
time, and the
expansion factor
.
One can measure this behavior using the stopping time, the total stopping
time, and the
expansion factor
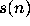 defined by
defined by

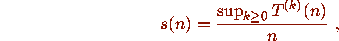 if n has a bounded trajectory and
if n has a bounded trajectory and 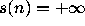 if n has a divergent
trajectory.
For example n = 27 requires 70 iterations to arrive at the value 1 and
if n has a divergent
trajectory.
For example n = 27 requires 70 iterations to arrive at the value 1 and

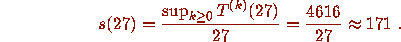 Table 1 illustrates the concepts defined so far by giving data on the
iterates
Table 1 illustrates the concepts defined so far by giving data on the
iterates 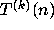 for selected values of n.
for selected values of n.